Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability. It happens when the brain does not get enough blood or oxygen. Knowing the main types of strokes – Ischemic, hemorrhagic, and transient – helps in understanding the risks, warning signs, and ways to prevent.
The brain is the control center of our entire body. Everything we do – from heartbeat, breathing, movement, to emotions, learning, memory, and decision-making. Unlike other organs, the brain can not store energy for later use; it constantly needs a rich supply of oxygen and nutrients from the blood to work properly. Even a small reduction in blood supply can affect our blood cells. It can lead to serious damage.
According to the World Health Organisation, 15 million people worldwide are suffering from a stroke annually.
Table of Contents
What is a stroke?
A stroke, often called a brain attack, is an emergency condition that occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain suddenly stops or is interrupted. Due to the lack of blood supply, your brain cells cannot get oxygen and nutrients. Within minutes, brain cells of the affected area begin to die. It can lead to a lethal condition.
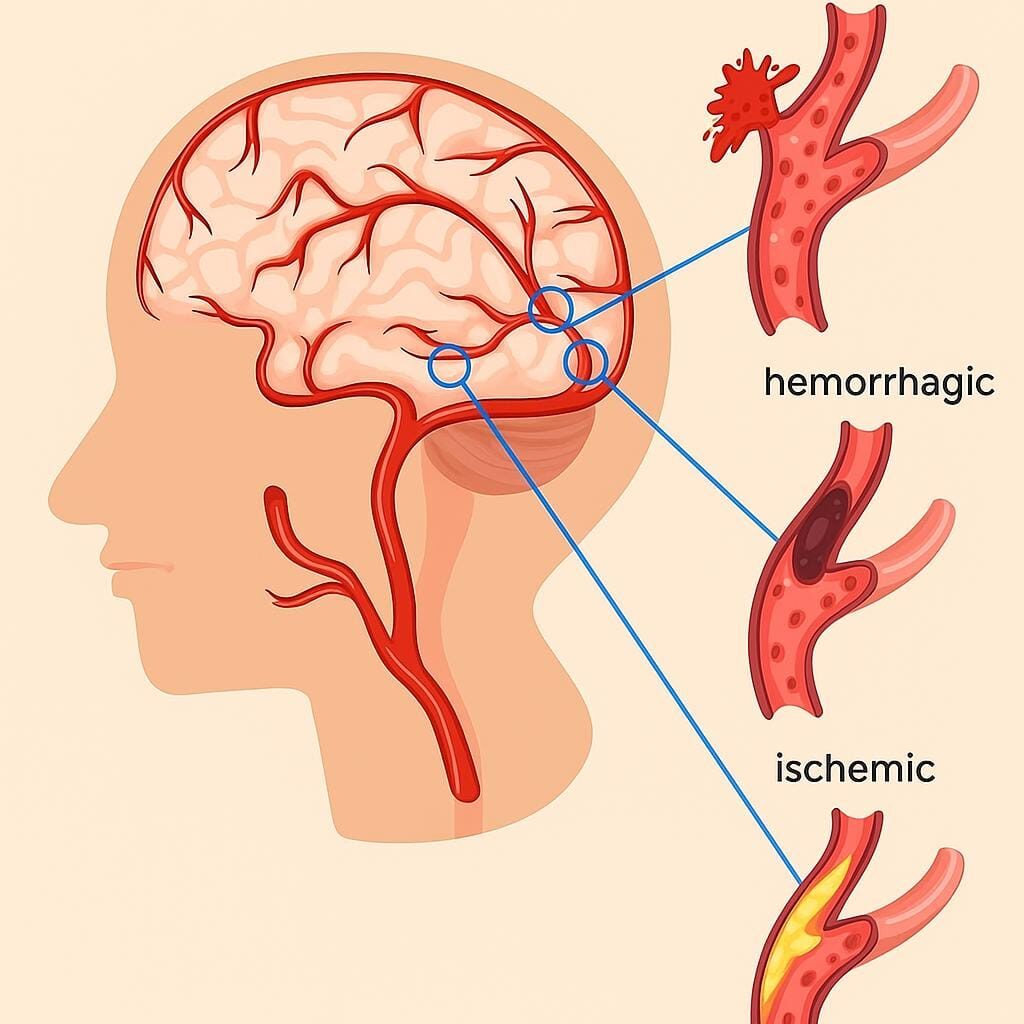
It can happen in two ways. They are:
Hemorrhagic:
It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks, causing bleeding inside or outside of the brain. The leaked blood puts pressure on nearby cells, causing severe damage to those cells. It is less common but more dangerous.
Ischemic:
It occurs when a plaque (fat deposits) or a clot blocks a blood vessel carrying blood to the brain. This is the most common type; almost 90% of all strokes are of this type.
Transient ischemic attack:
It occurs due to the same cause as blocked or narrowed blood vessels. Symptoms last only a few minutes or hours, but it is a red flag for future major strokes.
Symptoms:
- Weakness or tingling sensation in the arm, leg, or face on only one side of the body (paralysis)
- Difficulty in speaking or a complete loss of speech
- Blurred vision of one eye or both
- Loss of balance or coordination among body parts
- Sudden severe headache
Causes of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Brain tumors can burst suddenly, causing bleeding and damage to the brain cells
- Very high blood pressure can cause the rupture of a blood vessel
- Severe head injury
- Usage of some medications to make blood thinner
Causes of Ischemic & transient ischemic stroke:
The causes of both types of strokes are the same. They are:
- Blood clots
- Diabetes can increase plaque formation
- Uncontrolled blood pressure damages blood vessels
- Heart disease, such as a heart attack, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, can cause clots to travel to the brain.
Major Risk Factors that You Should Know:
- Risk increases with age.
- People with a family history of stroke or heart disease.
Some other risk factors can often be controlled. They are:
- Cholesterol levels can be managed.
- High blood pressure can be reduced.
- High sugar levels (diabetes) can be controlled.
- Quit alcohol consumption and smoking.
- Overweight can be reduced.
Prevention through Lifestyle changes
- Stay physically active: 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily, yoga, and meditation. Exercise can help reduce your weight, cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure, reducing salt (sodium) Intake, and eating a balanced diet.
- Maintain optimal cholesterol levels (score less than 200) by avoiding foods high in fat and fried foods, and choosing nuts, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Keep your blood sugar levels under control by reducing carbohydrate intake and consuming more fiber & nutrient-rich fruits and vegetables.
- Quit alcohol drinking and smoking.
Conclusion:
A stroke can strike without warning. But by recognizing early signs, risk factors, and causes, you can reduce the risk of it. By following healthy lifestyle choices, yoga, and meditation, it can be easily prevented. Thus, awareness and quick action can lower its impact.